TAIL ASYMPTOTICS OF SIGNAL-TO-INTERFERENCE RATIO
DISTRIBUTION IN SPATIAL CELLULAR NETWORK MODELS
Naoto Miyoshi
Tomoyuki Shirai
Abstract: We consider a spatial stochastic model of wireless cellular networks, where the base
stations (BSs) are deployed according to a simple and stationary point process on
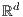 ,
, 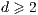 . In this model, we investigate tail asymptotics of the distribution of
signal-to-interference ratio (SIR), which is a key quantity in wireless communications. In the
case where the path-loss function representing signal attenuation is unbounded at the origin,
we derive the exact tail asymptotics of the SIR distribution under an appropriate sufficient
condition. While we show that widely-used models based on a Poisson point process
and on a determinantal point process meet the sufficient condition, we also give a
counterexample violating it. In the case of bounded path-loss functions, we derive a
logarithmically asymptotic upper bound on the SIR tail distribution for the Poisson-based
and
. In this model, we investigate tail asymptotics of the distribution of
signal-to-interference ratio (SIR), which is a key quantity in wireless communications. In the
case where the path-loss function representing signal attenuation is unbounded at the origin,
we derive the exact tail asymptotics of the SIR distribution under an appropriate sufficient
condition. While we show that widely-used models based on a Poisson point process
and on a determinantal point process meet the sufficient condition, we also give a
counterexample violating it. In the case of bounded path-loss functions, we derive a
logarithmically asymptotic upper bound on the SIR tail distribution for the Poisson-based
and 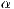 -Ginibre-based models. A logarithmically asymptotic lower bound with
the same order as the upper bound is also obtained for the Poisson-based model.
-Ginibre-based models. A logarithmically asymptotic lower bound with
the same order as the upper bound is also obtained for the Poisson-based model.
2010 AMS Mathematics Subject Classification: Primary: 60G55; Secondary:
90B18.
Keywords and phrases: Spatial point processes, cellular networks, tail asymptotics,
signal-to-interference ratio, determinantal point processes.