FINITE DIFFERENCE EQUATIONS AND CONVERGENCE RATES IN THE
CENTRAL LIMIT THEOREM
Abstract: We apply the theory of finite difference equations to the central limit
theorem, using interpolation of Banach spaces and Fourier multipliers. Let
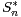 be a
normalized sum of i.i.d. random vectors, converging weakly to a standard normal vector
be a
normalized sum of i.i.d. random vectors, converging weakly to a standard normal vector
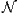 . When
does
. When
does 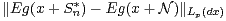 tend to zero at a specified rate? We show that, under moment conditions, membership of
tend to zero at a specified rate? We show that, under moment conditions, membership of
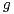 in
various Besov spaces is often sufficient and sometimes necessary. The results extend to
signed probability.
in
various Besov spaces is often sufficient and sometimes necessary. The results extend to
signed probability.
2000 AMS Mathematics Subject Classification: Primary: 46B70, 60F05, 65M06;
Secondary: 35K05, 42B15, 65M15;
Key words and phrases: Finite difference equations, central limit theorem, convergence
rate, interpolation theory, Fourier multipliers, Besov spaces, signed probability.